Automotive key manufacturing process (1) - welding
Welding is a necessary process in modern machinery manufacturing and is widely used in automobile manufacturing. Definition of welding: Welding refers to a process of forming a permanent joint by heating or pressurizing, or a combination of both; adding or not adding a filler; and bringing the two separated metal surfaces into an atomic bond. Welding method classification 2, commonly used welding methods and their advantages and disadvantages spot welding Part of the electric resistance welding, the workpiece to be welded is pressed between the two electrodes, and the current is passed through, and the electric resistance generated by the electric current passing through the contact surface of the workpiece and the adjacent region is locally heated to be melted into a plastic state, so that A connection that forms a metal bond. Spot welding is a high-speed, economical connection method. It is suitable for the manufacture of thin plate members which can be lapped, joints which are not required to be airtight and have a thickness of less than 3 mm. Spot welding requires metal to have good plasticity. This method is widely used in the welding of low carbon steel products such as automobile casings, fittings and furniture. Ultrasonic plastic welding is to transmit high-frequency mechanical vibrations through the workpiece to the interface part to accelerate the movement of the molecules. The molecular friction is converted into heat to dissolve the plastic at the interface, so that the two weldments are truly integrated into one another by molecular coupling. Because this molecular motion is done in an instant, most of the ultrasonic plastic welding can be completed in 0.25 to 0.5 s. Plasma refers to a gas whose temperature exceeds 3000 ° C under standard atmospheric pressure. It can be regarded as the fourth state of matter after solid, liquid and gaseous in the temperature spectrum. Plasma arc welding is a welding method developed on the basis of tungsten argon arc welding. The heat source for plasma arc welding is to obtain a higher ionization arc plasma after compressing and strengthening the free tungsten arc, which is called a plasma arc, also called a compression arc. Komatsu Swing Parts,Komatsu Swing Gearbox Parts,Komatsu Swing Motor Parts,Komatsu Excavator Swing Parts JINING SHANTE SONGZHENG CONSTRUCTION MACHINERY CO.LTD , https://www.stszcmparts.com
main content:
I. Definition and classification of welding II. Common welding methods and their advantages and disadvantages III. Welding defects and their control methods IV. New technologies and new directions for automotive welding I. Definition and classification of welding 
Common welding methods are fusion welding, pressure welding and brazing. The detailed classification methods are shown in the following table.
Fusion welding: During the welding process, the welded joint is molten to a molten state. Since the workpieces to be welded are closely attached together, under the action of temperature field, gravity, etc., without the pressure, the melt melted by the two workpieces may be mixed. After the temperature is lowered, the molten portion is condensed, and the two workpieces are firmly welded together to complete the welding method.
Pressure welding: A method of welding by applying a certain pressure during welding. Pressure welding is also called pressure welding. Forging, contact welding, friction welding, gas pressure welding, cold pressure welding, and explosion welding are areas of pressure welding.
Brazing: using a metal material with a lower melting point than the base material as a brazing filler metal, heating the weldment and the brazing material to a temperature higher than the melting point of the brazing filler metal, lower than the melting temperature of the base metal, and moisturizing the base material with a liquid brazing filler metal to fill the joint gap and A method of interconnecting a base material to achieve a joint weldment. 

Electric welding schematic
advantage:
l The nugget is always surrounded by a plastic ring when it is formed. The molten metal is isolated from the air and the metallurgical process is simple.
l The heating time is short and the heat is concentrated, so the heat affected zone is small, and the deformation and stress are also small. It is usually not necessary to arrange correction and heat treatment work after welding.
l There is no need to fill metal such as welding wire and welding rod, as well as welding consumables such as oxygen, acetylene and argon, and the welding cost is low.
l Easy to operate, easy to mechanize and automate.
l High productivity, low noise and no harmful gases.
Disadvantages and limitations:
l There is still no reliable non-destructive testing method. The quality of welding can only be checked by the destructive test of workpiece specimens and workpieces. It is guaranteed by various monitoring and monitoring techniques.
The l-point, seam-welded lap joint not only increases the quality of the component, but also forms a sharp corner around the nugget between the two plates, resulting in lower tensile strength and fatigue strength of the joint.
l The equipment has high power, high mechanization and high degree of automation, which makes the equipment costly and maintenance difficult.
MIG welding 
MIG gas arc welding is a welding method in which a continuous constant velocity feed of an arc between a meltable wire and a weldment is used as a heat source to melt the wire and the base metal to form a weld pool and a weld. In order to obtain a good weld, an applied gas should be used as an arc medium to protect the molten droplets, the molten pool metal and the high temperature metal in the weld zone from the harmful effects of the surrounding air.
advantage:
The lGMAW method can weld all metals and alloys.
l Overcome the limitation of the length of the electrode arc welding strip.
l Can perform all-position welding.
l The arc has a high deposition rate.
l High welding speed.
l The welding wire can be fed continuously, so there is no intermediate joint for the long weld.
l Due to the small amount of slag produced, the post-weld cleaning work can be reduced.
l It is a low hydrogen welding method.
l Welding operation is simple, easy to operate and use.
l shortcomings and limitations:
l The welding equipment is complicated, the price is expensive and it is not easy to carry.
l Due to the large welding torch, the accessibility in the narrow place is not good, thus affecting the protective effect.
l The outdoor wind speed should be less than 1.5m/s, otherwise it will easily produce air holes, so the outdoor welding should adopt the main wind measures.
lGMAW is an arc welding, and care should be taken to prevent radiation and arcing.
Stud welding: 
The method of welding metal studs or similar metal fastenings (plugs, nails, etc.) to a workpiece (typically a plate) is called stud welding. Stud welding technology is a specialized welding technology developed to improve welding quality and efficiency. Through the stud welding method, we can weld the columnar metal to the surface of the metal base material in a short time of 5ms~3s, and the weld seam is full-face fusion. This technology is widely used in the automotive industry due to its short welding time, high welding arc, concentrated welding energy, convenient operation, high welding efficiency and low thermal damage to the base metal. The methods for implementing stud welding include resistance welding, friction welding, explosion welding, and arc welding.
advantage:
l The welding time is short, only 1-3ms, the air is too late to invade the welding zone, the welded joint has been formed, so no protective measures are needed.
l The ratio of the diameter of the stud to the wall thickness of the workpiece to be welded can reach 8-10, and the minimum plate thickness is about 0.5mm.
l The weld shrinkage of the stud length is not considered, because the bath is small and the joint is plastically connected.
l The joint has no externally visible solder fillet, no need to check the appearance quality of the joint, and there are no defects such as pores and cracks.
TIG welding 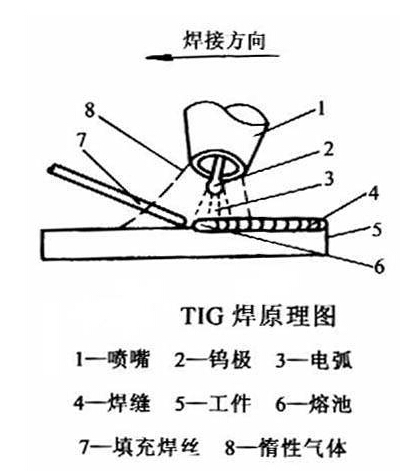
Under the protection of an inert gas, the welding process of melting the base material and filling the wire by the arc heat generated between the electrode and the base metal (workpiece) is utilized.
advantage:
l The inert gas does not react with any metal and is not soluble in metal, which provides good conditions for obtaining high quality welds.
l The welding process has good performance, bright arc, can observe the arc and the molten pool, even if the arc is still stable under a small current, the welding process has no splash and the weld is beautifully formed.
l Easy to adjust and control the welding heat input, suitable for thin plates or welding of heat sensitive materials.
l The arc has a cathode cleaning effect.
l Suitable for all-position welding, it is an ideal method to achieve double-sided forming of single-sided welding.
Disadvantages and limitations:
l The penetration depth is shallow, the welding speed is slow, and the welding productivity is low.
l The tungsten current carrying capacity is limited. Excessive current will reduce the mechanical properties of the welded joint, especially the plasticity and impact toughness.
l The surface of the workpiece is required to be high.
l The protective effect of gas during welding is greatly affected by the surrounding airflow, and protective measures are required.
l Higher production costs.
Projection welding: 
The same as spot welding, the projection welding is the resistance welding. The difference between the projection welding and the spot welding is that the projection welding needs to prefabricate the bumps of a certain shape and size. The size of the current passage area during the welding process is determined by the bump size. It is not determined by the electrode end face size like spot welding.
Advantages (compared to spot welding):
l Simultaneous welding of multiple solder joints at the same time, not only high productivity, but also no shunting effect.
l Current is denser than bumps. Compared with spot welding, the welding current distribution is more concentrated, so it can be welded with a smaller current and can reliably form a smaller nugget.
l The position of the bump is accurate, the size is the same, and the intensity of each point is relatively uniform.
l The wear of the electrode is smaller than spot welding, thus greatly reducing the maintenance and repair costs of the electrode.
l Compared with spot welding, oil, rust, oxide scale, coating and other coatings on the surface of the workpiece have less effect on the projection welding.
l It is possible to weld some thickness combinations that are difficult to weld by spot welding.
Disadvantages and limitations (compared to spot welding):
l Additional steps are required to punch the bumps.
l Sometimes the electrodes are more complicated.
l When welding multiple solder joints at the same time, it is necessary to use a high-power welder with high electrode pressure and high mechanical precision.
3. Welding defects and their control methods 1. Unfused is mainly the part between the weld metal and the base metal or between the weld bead metal and the bead metal, that is, the filler metal is stuck on the base material or the filler metal. Some of the layers are not fused together.
Preventive measures:
l slightly reduce the welding speed, slightly increase the welding current, so that the heat is increased enough to melt the base metal or the previous layer of weld metal;
l The angle of the electrode and the transport bar should be appropriate. The temperature and melting of the base material should be taken care of. For the unfused by the slag and dirt, it is necessary to strengthen the slag and clean the dirt such as oxide scale;
l Pay attention to the slag and molten iron. When the electrode is eccentric, adjust the angle so that the arc is in the correct direction.
l Gas shielded welding should control the welding speed not too high, the arc voltage is low, maintain a certain arc length, maintain the jet transition, and preferentially apply the helium mixed gas as the shielding gas;
l For semi-automatic or submerged arc automatic welding, the wire is directly aligned with the root of the joint to ensure the root penetration.
2. The undercut is the process of welding. After the arc melts the edge of the weld, it is not supplemented by the filler metal, and grooves or depressions are formed in the weld toe region or the root region of the weld metal.
Preventive measures:
l Use a suitable current to avoid excessive current;
l Control the welding speed so that the weld metal to be welded must be completely filled in all the melted parts of the base metal;
l When using the swinging process, the strip is slightly slower at the edge of the groove, and the electrode should be stopped for a short time so that the temperature between the weld metal and the adjacent sheet is similar, and the speed of the strip is faster in the middle of the groove. Mixing the filler metal with the base metal evenly;
l Manual welding should control the position of the welding rod. In the fillet welding, the welding rod should adopt a proper angle and maintain a certain arc length to keep the moving rod evenly, not only to ensure complete melting, but also to form a full shape of the welding molten pool;
l use short arc welding as much as possible;
l When it is possible to form excessive undercuts, it should be avoided to weld the fillet welds in the horizontal position and use the ship-shaped position welding;
l Excessive oscillating is also easy to form undercuts, and multiple defects can be used to overcome this defect.
3. Welded tumors are excessive weld metal flowing out of the base metal melting surface without fusion. This metal is formed because the molten pool temperature is too high, causing the liquid metal to solidify slowly and falling under its own weight. That is, during the welding process, the molten metal flows to the metal tumor formed on the unmelted base metal outside the weld. More frequent occurrences in fillet welds than butt welds.
Preventive measures:
l The process parameters should be correctly selected, the gap should not be too large, and the welding current of 10%~15% smaller than the flat welding should be selected, and the temperature of the molten pool should be strictly controlled to prevent too high;
l Use small-diameter welding rods for welding, the welding rods swing to the middle faster, the sides are slightly slower, and there is a slight arcing action time at the edge;
l When docking the first layer, pay attention to the bath temperature and closely observe the shape of the bath. If it is found that there is a sign of falling, it should immediately extinguish the arc, let the temperature of the molten pool drop slightly, and then lead arc welding;
l Choose a suitable electrode inclination angle. When using alkaline welding rods, short arc welding should be used, and the speed of the moving rod should be uniform.
4. The crater arc pit is a depression formed at the end of the weld due to improper arcing or arcing, and is not eliminated before the subsequent weld welding or during the subsequent weld welding. The crater usually appears at the end of the weld or At the joint, the crater not only weakens the weld cross section, but also has a tendency to accumulate impurities due to the high cooling rate, and is accompanied by defects such as pores, slag inclusions, cracks, and the like.
Preventive measures:
l correctly select the welding current;
l Adopting intermittent arc extinguishing method or using arc-receiving plate to lead the arc pit to the outside of the weldment;
l Manual arc welding During the arc-receiving process, the electrode stays at the end of the tail for a short time or several round trips, so that enough electrode metal fills the molten pool;
l In the automatic submerged arc welding, press the “stop†button in two steps in order to fill the crater.
5. After the pit welding, a local low-lying portion which is lower than the surface of the base material is formed on the surface or the back surface of the weld, and the pit on the back surface of the weld is usually called a concave.
Preventive measures:
l Short arc length, adjust the inclination angle of the electrode and appropriately reduce the assembly gap;
l The electrode stays for a little longer at the end. In order to avoid the temperature of the molten pool being too high due to excessive residence time, and the molten pool is too large or welded, it should be filled with several intermittent arc extinguishing. After a short stay, the arc is extinguished. After it is slightly cold, the arc is led and filled with some molten metal, so that the pit can be filled several times. However, the alkaline DC welding rod should not adopt the intermittent arc extinguishing method, otherwise it will easily produce pores.
6. Incomplete penetration is a partial unfused phenomenon between basic metals or between a base metal and a deposited metal. It is somewhat similar to unfused, and sometimes difficult to distinguish.
Preventive measures:
l Correctly select the groove type and assembly clearance, pay attention to the cleaning between the sides of the groove and the welding layer;
l correctly select the size of the welding current;
l Adjust the angle of welding in the moving bar at any time to fully fuse the molten metal and the molten metal and the base metal;
7. During the sintering process, the molten metal flows out from the back of the groove to form a defect of the perforation.
Preventive measures:
l reduce the welding current and increase the welding speed appropriately;
l Strictly control the weldment clearance and ensure the consistency of this gap over the entire length of the weld.
Fourth, new technology of automotive welding and new directions of laser welding technology 
Laser welding is a highly efficient and precise welding method in which a focused laser beam is used as an energy source to bombard the heat generated by the weldment. The welding process is a heat conduction type, that is, the laser radiation heats the surface of the workpiece, and the surface heat is diffused to the inside through heat conduction. By controlling parameters such as the width, energy, peak power and repetition frequency of the laser pulse, the workpiece is melted to form a specific molten pool. Due to its unique advantages, it has been successfully applied to precision welding of small and small parts.
The characteristic of laser welding is that the workpiece to be welded has very little deformation, almost no joint gap, and the welding depth/width ratio is high, so the welding quality is higher than the conventional welding method. In the automotive industry, laser technology is mainly used for body welding, welding and parts welding.
Plastic welding technology 
Branson plastic welding technology has been successfully used in automotive warranty bars, instrument panels and dashboards, brake lights, direction indicators, automotive door panels and other engine-related parts manufacturing industries. In recent years, many of the traditional metal-used parts have also been replaced with plastics, such as intake pipes, instrument pointers, radiator reinforcement, fuel tanks, filters, and so on.
Energy-saving and control technology of resistance welding The development of three-phase low-frequency resistance welding machine, three-phase secondary rectification contact welding machine and IGBT inverter resistance welding machine can solve the problem of grid imbalance and improve power factor, and further save energy. Microcomputer control for parameter realization is better suited for welding aluminum alloy, stainless steel and other difficult-to-weld metals. In addition, the weight of the device can be further reduced.
Plasma welding (PAW) 
The plasma welding process is applied to the welding of the two semicircular edges of the tank. Argon-shielded plasma-welded cutting has long been used in various industries, mainly for alloy steel and non-ferrous metal processing. The engine valve body has long been plasma-welded with a fill ring. In the past ten years, powder plasma surfacing has been greatly developed, and it is possible to carry out fine surfacing of thin layers of small fusion ratio and to weld various special alloy surfaces.
TCP automatic zero calibration technology TCP automatic zero calibration is a new technology used in robot welding. Its hardware consists of a trapezoidal fixed support and a set of laser sensors. When the torch passes through the TCP holder in different postures, the laser sensor transmits the recorded data to the CPU for comparison and calculation with the initial set value. When the TCP deviates, the robot automatically runs the zero calibration program, automatically adjusts the angle of each axis, and restores the TCP zero in the least amount of time.
At present, this technology is adopted in the robot welding production line of the Polo Rear Bridge and the Passat sub-frame, which greatly facilitates equipment adjustment, saves adjustment time and improves product quality.
Weld seam automatic tracking technology 
The automatic seam tracking technology is arc voltage tracking sensing. The system has a reference point for finding the starting point, end point and arc length of the weld. During the welding process, the voltage is adaptively controlled by the arc sensor according to the change of the arc length. This method can only be applied to the form of angle joints. For a large number of thin plate lap welds of car chassis parts, it cannot be applied because the arc length reference point cannot be found.
Robot welding 
Industrial robots, which combine automatic production and flexible production characteristics, have been used in large and rapid use in recent years. In terms of welding, spot welding robots and arc welding robots are mainly used. The level of domestic automotive welding is quite different from that of foreign countries. The automation of welding has attracted the attention of domestic automobile manufacturers.